Composite Layup Project Background
Currently, 90% of composite sheet layup is completed manually; this manual process leads to low throughput, high ergonomic risk exposure, and high labor costs, , opening the door for automated composite layup as a high-value robotics project. While a Human Robot Collaborative (HRC) approach may seem like an alternate solution, current safety standards in HRC are structured either in a stop-and-go fashion, which can damage the composite materials, or use significantly slower robot movements, decreasing productivity. This project for robotics in manufacturing proposes an HRC approach to composite layups that uses the following innovations: a perception-based framework to estimate actions performed by a human, a planning system to select the robot action that better suits the estimated human actions, and an execution monitoring layer to track the state of the cell to prevent errors/collisions.
Composite Layup Project Objective
Create a safer, more productive process for composite layup through human-robot collaboration. The project outputs are expected to reduce layup time by 20% and improve overall layup productivity by 10% while reducing human ergonomic exposure by 50%.
Composite Layup Project Technical Approach
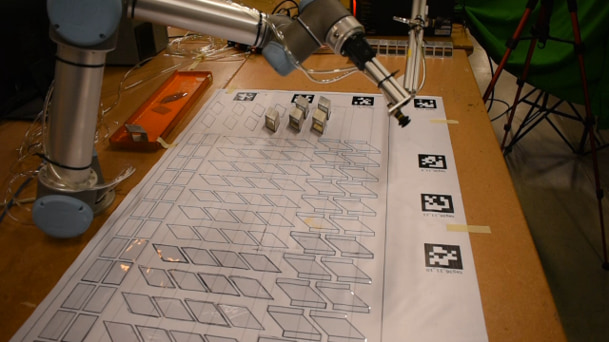
The expected project outputs include:
- hybrid cell to support human-robot collaboration
- visual perception analytics framework to estimate actions being performed by humans, drive constraints across tasks, and perform robot pose estimation and environment representation
- planning system to determine suitable robot base positions to perform the tasks, select the robot action that suits the estimated human action, and generate low-level instructions for the robot to grasp and position objects
- an execution monitoring layer to track the state of the cell to prevent errors/collisions
Composite Layup Project Participants
United Technologies Research Center (UTRC) (Principal Investigator), University of Southern California
